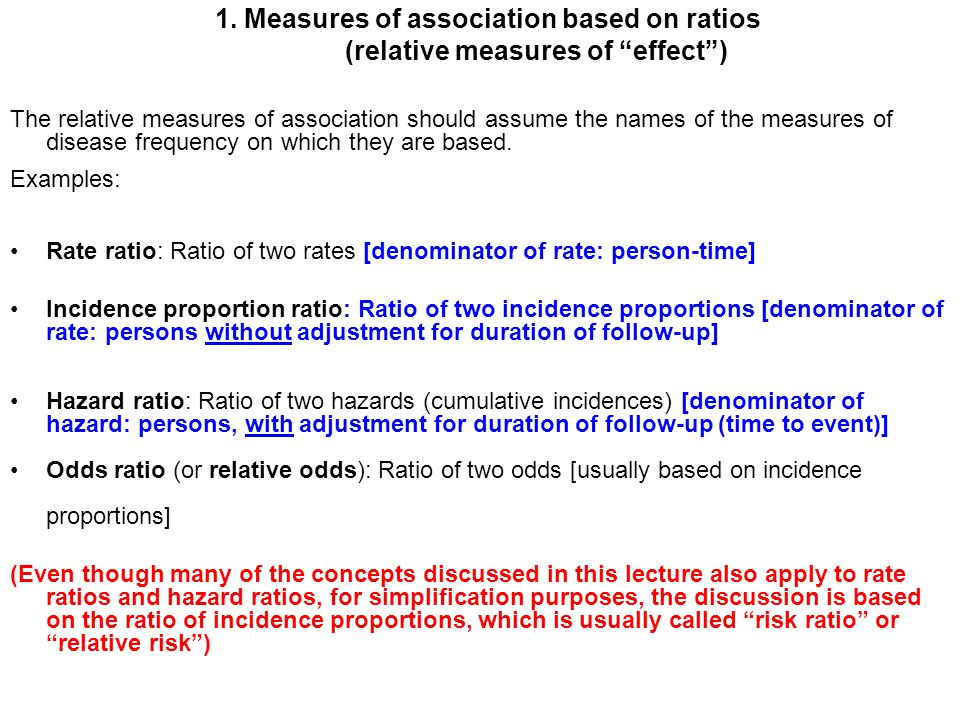
An Odds Ratio (OR) then is simply the comparison of two odds, OR=Odds (A)/Odds (B) The Relative Risk (RR) is simply the comparison of two risks or probabilities, RR=Probability (A)/Probability (B) This is made more clear when the term is referred to as the Risk Ratio Let's look at this graphically0 increased risk log OR = 0 no difference in risk log OR <Relative Risk and Odds Ratio for the obese 3) Overall, you can see that decreasing the baseline incidence will decrease the odds ratio (300 in those who are nonobese versus 129 in those who are obese) Obviously, these results run counter to expected results, putting the onus on the researcher to justify them Similarly, you should find that increasing the incidence will increase

Calculation Of Relative Risks Rr And Odd Ratios Or Download Table
Relative risk versus an odds ratio
Relative risk versus an odds ratio-Odds Ratio versus Relative Risk Since it is a ratio of ratios, the odds ratio is very difficult to interpret The relative risk is easier to interpret, so the odds ratio alone is not very helpful However, there are certain commonly occurring situations in which the estimate of the relative risk is not very good, and the odds ratio can be usedFor more common outcomes, the odds ratio always overstates the relative risk, sometimes dramatically




Relative Risk And Odds Ratio
Odds ratio (OR) and risk ratio (RR) are two commonly used measures of association reported in research studies In crosssectional studies, the odds ratio is also referred to as the prevalence odds ratio (POR) when prevalent cases are included, and, instead of the RR, the prevalence ratio (PR) is calculatedThe simple relative risk is 055 and the simple odds ratio is 025Clearly the probability of fathering a child is strongly dependent on a variety of demographic variables, especially age (the issue of marital status was dealt with by a separate analysis) The control group was 84 years older on average (435 years versus 351), showing the need to adjust for this variableYes and no The risk ratio is collapsible, so adjusting for any variable that is not associated with either the exposure or outcome should not change the magnitude of the risk ratio In addition, the summary risk ratio across strata should be between the values of the stratumspecific risk ratios (something that does not hold with the odds ratio)
Odds ratio and relative riskThe odds ratio supports clinical decisions by providing information on the odds of a particular outcome relative to the odds of another outcome In the endocarditis example, the risk (or odds) of dying if treated with the new drug is relative to the risk (odds) of dying if treated with the standard treatment antibiotic protocolOdds ratio vs risk ratio You know the difference between risk and odds A risk is the proportion of subjects with an event in a total group of susceptible subjects Thus, we can calculate the risk of having a heart attack among smokers (infarcted smokers divided by the total number of smokers) and among nonsmokers (the same, but with non
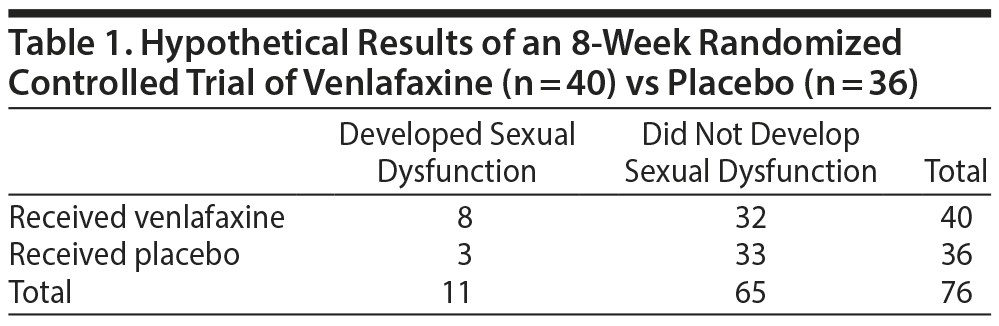
Subsequently, the term relative risk commonly refers to either the risk ratio or the odds ratio However, only under certain conditions does the odds ratio approximate the risk ratio Figure 1 shows that when the incidence of an outcome of interest in the study population is low (<10%), the odds ratio is close to the risk ratio However, theThe ratio of these is the risk ratio, a relative measure of association Risk Ratio = CI e /CI u = 090/058 = 155 Interpretation Smokers had 155 times the risk of respiratory disease compared to nonsmokers over an 18 year period of observation Using the same cumulative incidences we can calculate the risk difference, an absolute measureIn a control group The odds ratio (OR) is the odds of an event in an experimental group relative to that in a control group An RR or OR of 100 indicates that the risk is comparable in the two groups A value greater than 100 indicates increased risk;



Analytical Studies



Relative Risk Ratios And Odds Ratios
Odds ratio versus relative risk Since it is a ratio of ratios, the odds ratio is very difficult to interpret The relative risk is easier to interpret, so the odds ratio alone is not very helpful However, there are certain commonly occurring situations in which the estimate of the relative risk is not very good and the odds ratio can be usedOdds ratio), in which p0 is the outcome prevalence (risk) among the unexposed Some have applied this formula to an adjusted odds ratio to obtain an adjusted risk ratio 49 This method can produce biased risk ratios and incorrect confidenceWhen the outcome of interest is relatively rare (<10%), then the odds ratio and relative risk will be very close in magnitude In such a case, investigators often interpret the odds ratio as if it were a relative risk (ie, as a comparison of risks rather than a comparison of odds which is less intuitive)




Odds Ratios And Risk Ratios Youtube



Interpretation Of Odds Ratio And Fisher S Exact Test By Sergen Cansiz Towards Data Science
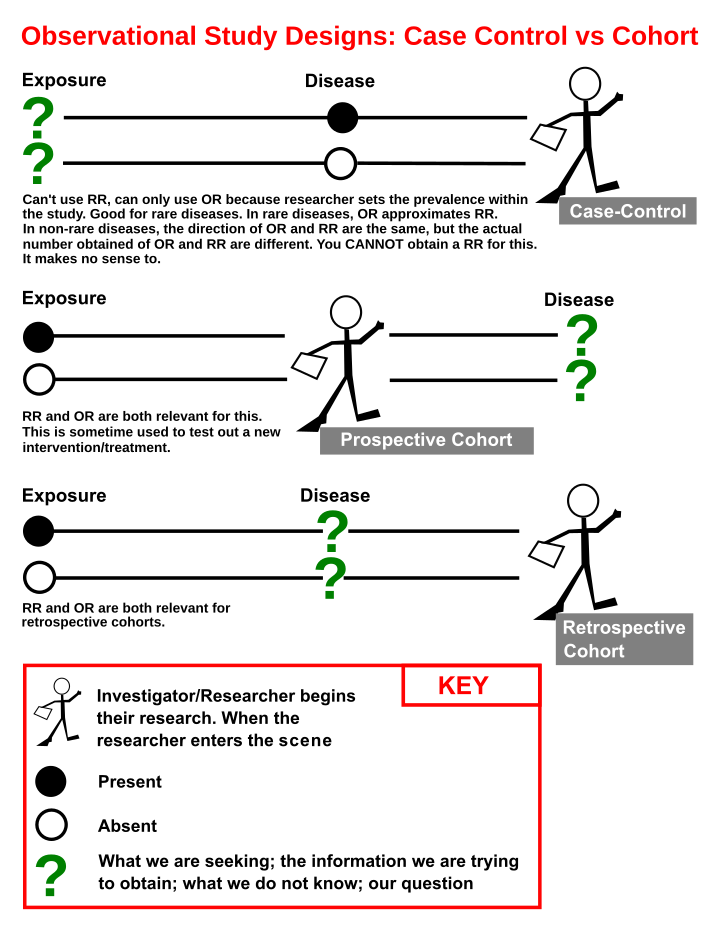
When the disease is rare, the odds ratio will be a very good approximation of the relative risk The more common the disease, the larger is the gap between odds ratio and relative risk In our example above, p wine and p no_wine were 0009 and 0012 respectively, so the odds ratio was a good approximation of the relative risk OR = 0752 and RR = 0751 suggests a reduced risk inIn practice the odds ratio is commonly used for casecontrol studies, as the relative risk cannot be estimated In fact, the odds ratio has much more common use in statistics, since logistic regression, often associated with clinical trials, works with the log of the odds ratio, not relative risk




Chapter 6 Choosing Effect Measures And Computing Estimates Of Effect Cochrane Training



Http Www Floppybunny Org Robin Web Virtualclassroom Stats Basics Part13 Risks Rates Odds Pdf
63 Risk, Relative Risk and Odds In this section, we will introduce some other measures we can find using a contingency table One of the most straightforward measures to find is the risk of any given event The probability that an event will occur In simple terms, a risk for a group is the same as the proportion of success for aThe Relative Risk Ratio and Odds Ratio are both used to measure the medical effect of a treatment or variable to which people are exposed The effect could be beneficial (from a therapy) or harmful (from a hazard) Risk is the number of those having the outcome of interest (death, infection, illness, etc) divided by the total number exposed toThe odds ratio will be greater than the relative risk if the relative risk is greater than one and less than the relative risk otherwise In the example above, if the adjusted odds ratio were interpreted as a relative risk, it would suggest that the risk of antibiotic associated diarrhoea is reduced by 75% for the intervention relative to the placebo group



Confluence Mobile Wiki Ucsf
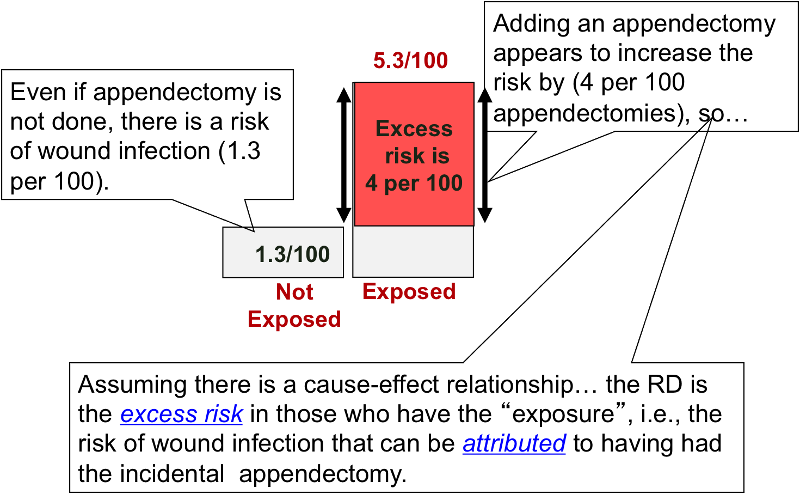



Risk Differences And Rate Differences
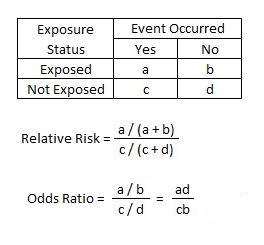
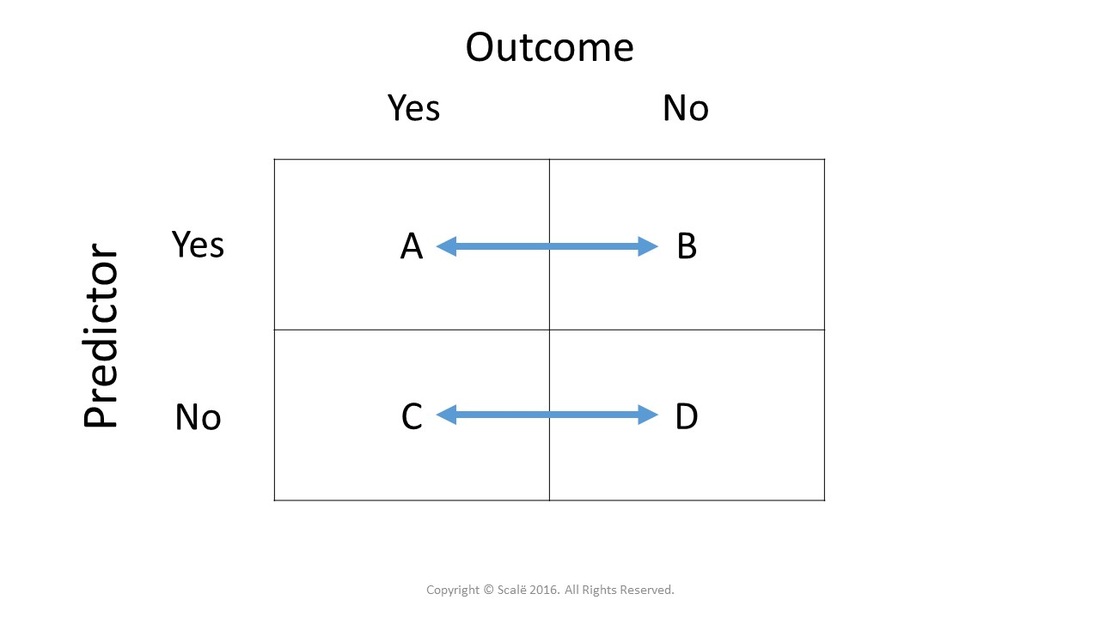
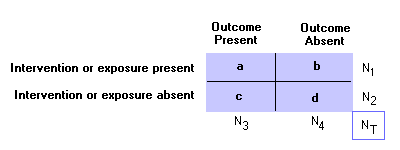
Odds ratio = (A*D) / (B*C) The relative risk tells us the ratio of the probability of an event occurring in a treatment group to the probability of an event occurring in a control group It is calculated as Relative risk = A/ (AB) / C/ (CD) In short, here's the difference An odds ratio is a ratio of two odds1 we can calculate relative risk IF we can estimate probabilities of an outcome in EACH group 2 we can't do that in case control studies 3 we can calculate the odds ratio even if we don't know the probabilities in the groups It would then be nice, if odds ratio was close to relative riskPute either the odds ratio or the relative risk to answer this question The odds ratio compares the relative odds of death in each group For women, the odds were exactly 2 to 1 against dying (154/308 05) For men, the odds were almost 5 to 1 in favor of death (709/142 4993) The odds ratio is 9986 (4993/05) There is a 10fold greater
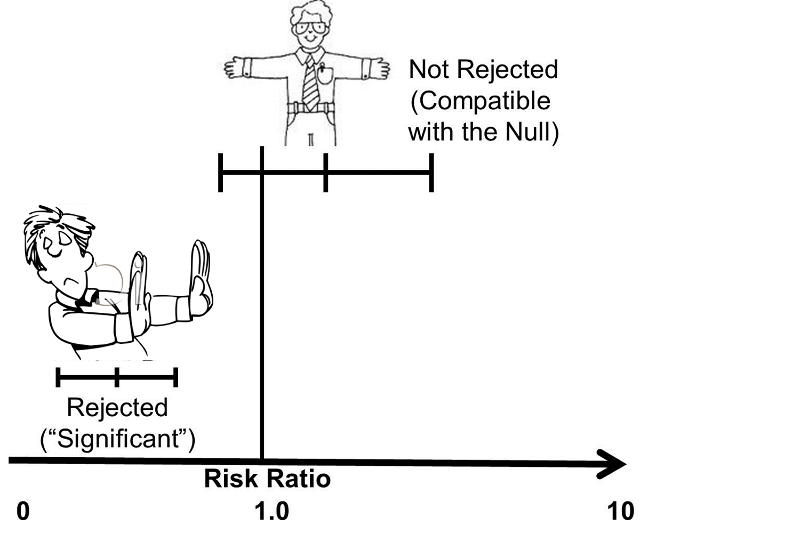



Confidence Intervals And P Values



Epidemiology Stepwards
Relative risk and odds ratio An RR (or OR) more than 10 indicates an increase in risk (or odds ) among the exposed compared to the unexposed, whereas a RR (or OR) <10 indicates a decrease in risk (or odds ) in the exposed groupA crude odds ratio can be converted to a crude risk ratio risk ratio = odds ratio/(1 − p0) (p0 ×0 decreased risk Odds Ratio 0 5 10 15 More on the Odds Ratio Log Odds Ratio4 2 0 2 4




Relative Risk Wikipedia




The Difference Between Relative Risk And Odds Ratios The Analysis Factor
1 suggests an increased risk of that outcome in the exposed group A risk ratio <The basic difference is that the odds ratio is a ratio of two odds (yep, it's that obvious) whereas the relative risk is a ratio of two probabilities (The relative risk is also called the risk ratio) Let's look at an example Relative Risk/Risk Ratio Suppose you have a school that wants to test out a new tutoring programRelative Risk Risk is based on proportion of persons with disease = cumulative incidence Risk ratio = ratio of 2 cumulative incidence estimates = relative risk Since all of the measures are ratios, either of probabilities or of odds, it is clearer and simpler to use the word ratio in describing each type



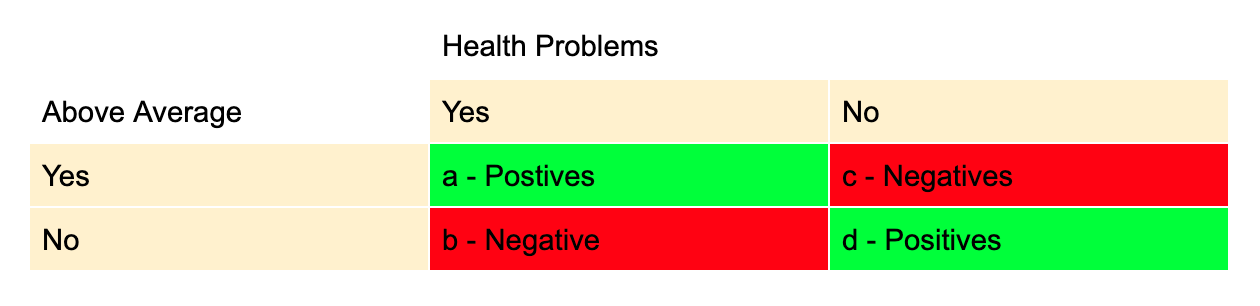
Silo Tips Download Transcript Measuring Risk In Epidemiology B D A C Measuring Risk In Epidemiology




Odds Ratios Vs Risk Ratios Stats By Slough
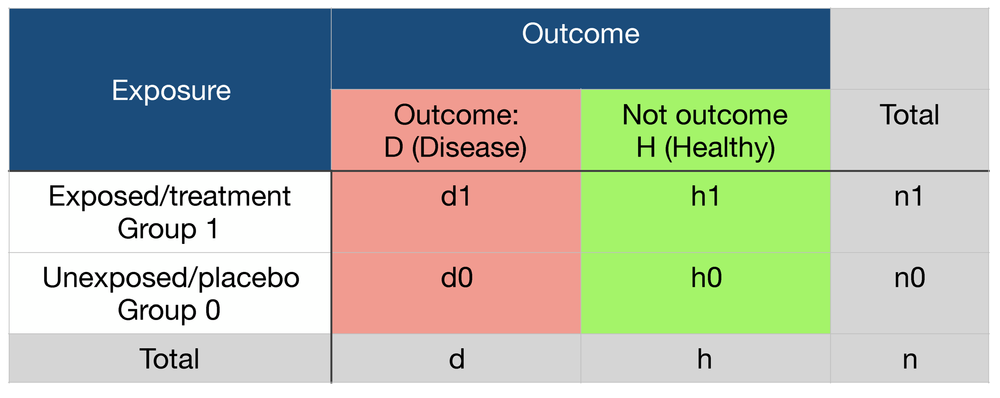
This is compared to the relative risk which is (a / (ab)) / (c / (cd)) If the disease condition (event) is rare, then the odds ratio and relative risk may be comparable, but the odds ratio will overestimate the risk if the disease is more commonRelative risk, Risk difference and Odds ratio When the data to be analyzed consist of counts in a crossclassification of two groups (or conditions) and two outcomes, the data can be represented in a fourfold table as follows Several statistics can be calculated such as relative risk and risk difference, relevant in prospective studies, andA value lower than 100 indicates decreased risk The 95% confidence intervals and statistical




Literature Search



Relative Risk Article
Sometimes, we see the log odds ratio instead of the odds ratio The log OR comparing women to men is log(144) = 036 The log OR comparing men to women is log(069) = 036 log OR >Odds Ratio (OR) is a ratio or proportion of odds I just remember that odds ratio is a ratio of odds and probability isn't a ratio of odds (AKA it is the other option) Relative Risk = Probability / Probability Odds Ratio = Odds / Odds Now that you have a general idea of what odds ratio and relative risk are you need to know when to useEven with initial risks as high as 50% and very large reductions in this risk (odds ratios of about 01), the odds ratio is only 50% smaller than the relative risk (01 for the odds ratio compared with a true value for the relative risk of 02)




Relative And Attributable Risks Absolute Risk Involves People




Math Formula To Reproduce A Plot Comparing Relative Risk To Odds Ratios Cross Validated
Odds ratios (OR) are commonly reported in the medical literature as the measure of association between exposure and outcome However, it is relative risk that people more intuitively understand as a measure of association Relative risk can be directly determined in a cohort study by calculating a risk ratio (RR)Both the odds ratio and the relative risk compare the relative likelihood of an event occurring between two groups The relative risk is easier to interpret and is consistent with general intuition Some designs, however, allow only for the calculation of the odds ration Covariate adjustment is easier for an odds ratioThe relative risk (also known as risk ratio RR) is the ratio of risk of an event in one group (eg, exposed group) versus the risk of the event in the other group (eg, nonexposed group) The odds ratio (OR) is the ratio of odds of an event in one group versus the



Med Mahidol Ac Th Ceb Sites Default Files Public Pdf Academic 16 Race611 Ebm Risk study 16 Vallibhakara sa 10 12 16 Print Pdf




On Biostatistics And Clinical Trials Odds Ratio And Relative Risk
The relative risk is the ratio of the risk in the exposed group to the risk in the unexposed group, as is summarized in Box 1 Depending on the study design and statistical method applied, the relative risk can be presented using different measures of effect, such as the incidence rate ratio and hazard ratioThe odds ratio (OR) is the ratio of the odds of cancer in smokers to the odds of cancer in nonsmokers OR = (a/b)/ (c/d) = (ad)/ (bc) The risk ratio (RR), also called the relative risk, is the ratio of the probability of cancer in smokers to the probability of cancer in nonsmokers Given that you know a, b, c, and d, you can compute either ofIf the risk ratio is 1 (or close to 1), it suggests no difference or little difference in risk (incidence in each group is the same) A risk ratio >




Measuring Of Risk



1
Odds ratio (OR) is a statistic commonly encountered in professional or scientific medical literature Most readers perceive it as relative risk (RR), although most of them do not know why thatA nonmemorization method of dealing with RR and OR*USMLE is a registered trademark of its respective holder I am in no way affiliated with itDisclaimerRELATIVE RISK AND ODDS RATIO Risk and Odds just seemed the same to me for a long time Since then, I have come to understand to important difference Lets start with Relative Risk Relative Risk can be addressed by asking the following question How many times more likely is an exposed group to develop a




Categorical Data Ziad Taib Biostatistics Astra Zeneca February



Studying Studies Part I Relative Risk Vs Absolute Risk Peter Attia
A risk ratio of 10 indicates identical risk among the two groups A risk ratio greater than 10 indicates an increased risk for the group in the numerator, usually the exposed group A risk ratio less than 10 indicates a decreased risk for the exposed group, indicating that perhaps exposure actually protects against disease occurrenceYou may have noticed that the odds ratio and relative risk are very similar in this case This happens when the proportions being compared are both close to 0 Which one you decide to use is a matter of personal preference and perhaps your audienceRisk ratios, odds ratios, and hazard ratios are three ubiquitous statistical measures in clinical research, yet are often misused or misunderstood in their interpretation of a study's results 1 A 01 paper looking at the use of odds ratios in obstetrics and gynecology research reported 26% of studies (N = 151) misinterpreted odds ratios as risk ratios 2, while a




Pdf What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios Semantic Scholar



Silo Tips Download Transcript Measuring Risk In Epidemiology B D A C Measuring Risk In Epidemiology
Unless I'm mistaken, the equation explained above does not properly describe Odds Ratio, it describes Relative Risk Odds Ratio is the odds that the diseased group was exposed, divided by odds that the nondiseased group was exposed (a/c)/(b/d) in the classic table Relative Risk is the risk of developing disease in the exposed/intervention



Understanding Relative Risk Odds Ratio And Related Terms As Simple As It Can Get Psychiatrist Com




Relative Risk Vs Odds Ratio On The Backpack And Back Pain Study Massage Fitness Magazine



What Is The Difference Between The Risk Ratio Rr And The Odds Ratio Or Quora




Risk Ratio Definition Formula How To Calculate



Forest Plots Of Relative Risks And Odds Ratios Of Detecting Fecal Download Scientific Diagram




Ppt The Odds Ratio Relative Odds Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 6056



1




Hazard Ratio Vs Odds Ratio ただの悪魔の画像



Calculate Relative Risk With 95 Confidence Intervals




What Is An Odds Ratio And How Do I Interpret It Critical Appraisal




How To Interpret And Use A Relative Risk And An Odds Ratio Youtube



Relative Risk Vs Odds Ratio Authorstream



Case Control Study Wikiwand




1 Relative Risks Odds Ratios Or Hazard Ratios Of Risk Factors For Download Table




Hazard Ratio Relative Risk Or Odds Ratio Of Selected Outcomes For The Download Table



Beaumont Cloud Cme Com Launchscorm Aspx Caseid 112 Userid 0 Video True




Relative Risk Odds Ratios Youtube



Measures Of Association Ppt Download




Measures Of Disease Association Measuring Occurrence Of New Outcome Events Can Be An Aim By Itself But Usually We Want To Look At The Relationship Between Ppt Download




When Can Odds Ratios Mislead The Bmj




Hsrp 734 Advanced Statistical Methods June 5 08




Odds Ratios Versus Relative Risk




Odds Ratio Relative Risk Calculation Definition Probability Odds Youtube




Using Odds Ratio In Case Control Studies Youtube




Estimating Risk
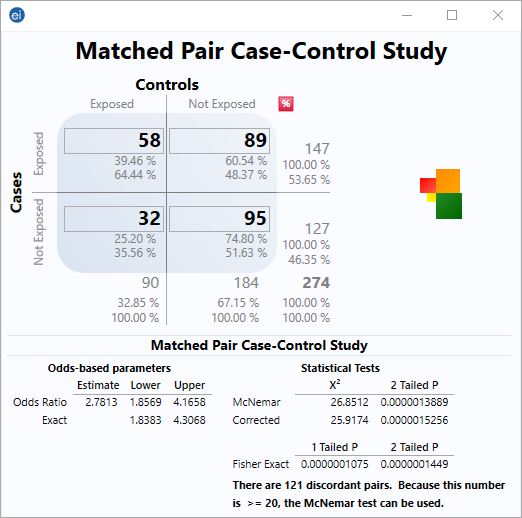



Matched Pair Case Control Statcalc User Guide Support Epi Info Cdc




Relative Risks And Odds Ratios What S The Difference Mdedge Family Medicine



6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 Review Incidence And Prevalence Are Formally Defined On Slide 7 Birth And Death Rates Are Also Estimates Of Absolute Risk Risk Factors Are Identified By Determining



Relative Risk Ratio Vs Odd Ratio Ppt Authorstream




Relative Risk Versus Odds Ratio Usmle Biostatistics 4 Youtube



Epidemiology Glossary Physical Diagnosis Skills University Of Washington School Of Medicine




Calculate Relative Risk With 95 Confidence Intervals




Pdf When To Use The Odds Ratio Or The Relative Risk Semantic Scholar




Odds Ratios Versus Relative Risk



Probability Odds Ratio And Relative Risk Gpraj



Ppt Odds Ratio Vs Relative Risk Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id



Mara Averick As Someone Who Asks For Odds Ratios And Relative Risk At The Vet I This Post How The Odds Ratio Confounds A Brief Study In A




Relative Risk And Odds Ratio




Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1




Kevin Whelan If You Re Struggling With Odds Ratios Relative Risks Standardised Mean Differences And Number Needed To Treat And The Associated Alphabet Soup Or Rr Smd Nnt Then This Paper




Relative Risk And Odds Ratio Usmle The Journey




A Most Odd Ratio Interpreting And Describing Odds Ratios Abstract Europe Pmc




A Most Odd Ratio Interpreting And Describing Odds Ratios Sciencedirect



Absolute Risk Vs Relative Risk Vs Odds Ratio Pp Made Easy On Vimeo




Numerators Denominators And Populations At Risk Health Knowledge




Odds Ratio Relative Risk By Susi Delaney




Effect Sizes Basicmedical Key




The Odds Ratio Calculation Usage And Interpretation Biochemia Medica




Pdf When To Use The Odds Ratio Or The Relative Risk



1




Measures Of Effect Relative Risks Odds Ratios Risk Difference And Number Needed To Treat Kidney International



Research Statistics Basics Contents 1 Basic Concepts 2 References Basic Concepts Null Hypothesis The Hypothesis That The Independent Variable Has No Effect On The Dependent Variable For Example Steroids Do Not Improve Outcomes In Ards Would Be



1




Believability Of Relative Risks And Odds Ratios In Abstracts Cross Sectional Study The Bmj




Calculation Of Relative Risks Rr And Odd Ratios Or Download Table



Http Www Floppybunny Org Robin Web Virtualclassroom Stats Basics Part13 Risks Rates Odds Pdf




Math Formula To Reproduce A Plot Comparing Relative Risk To Odds Ratios Cross Validated



Population Perspective Made Easy On Vimeo




Cph Exam Review Epidemiology Ppt Download




Relative Risk And Absolute Risk Definition And Examples Statistics How To




Relation Between The Odds Ratio Relative Risk And Baseline Risk




Statistics Part 13 Measuring Association Between Categorical Data Relative Risk Odds Ratio Attributable Risk Logistic Regression Data Lab Bangladesh




Relative Risk Wikipedia
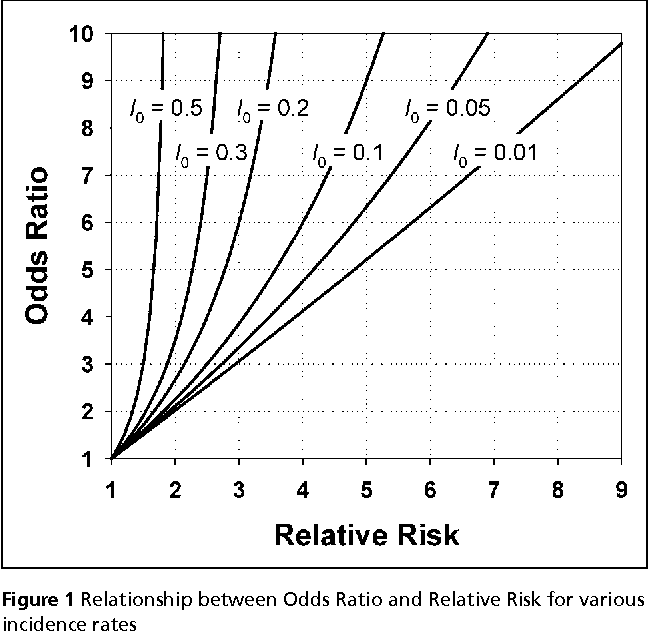



Pdf When To Use The Odds Ratio Or The Relative Risk Semantic Scholar




How To Calculate Odds Ratio And Relative Risk In Excel Statology




A Beginner S Guide To Interpreting Odds Ratios Confidence Intervals And P Values Students 4 Best Evidence



Confidence Interval For Relative Risk Ppt Video Online Download




Converting An Odds Ratio To A Range Of Plausible Relative Risks For Better Communication Of Research Findings The Bmj




Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1




Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios



Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1




On Biostatistics And Clinical Trials Odds Ratio And Relative Risk



Studying Studies Part I Relative Risk Vs Absolute Risk Peter Attia



Silo Tips Download Transcript Measuring Risk In Epidemiology B D A C Measuring Risk In Epidemiology




Glossary Of Research Terminology




Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios




33 Epidemiology Ideas Cohort Study Case Control Study Study Design



Research Statistics Basics Contents 1 Basic Concepts 2 References Basic Concepts Null Hypothesis The Hypothesis That The Independent Variable Has No Effect On The Dependent Variable For Example Steroids Do Not Improve Outcomes In Ards Would Be



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿